Most enterprises scaling agentic AI are overspending without knowing where the capital is going. This isn’t just a budget oversight. It points to deeper gaps in operational strategy. While building a single agent is a common starting point, the true enterprise challenge is managing quality, scaling use cases, and capturing measurable value across a fleet of 100+ agents.
Organizations treating AI as a collection of isolated experiments are hitting a “production wall.” In contrast, early movers are pulling ahead by building, operating, and governing a mission-critical digital agent workforce.
New IDC research reveals the stakes:
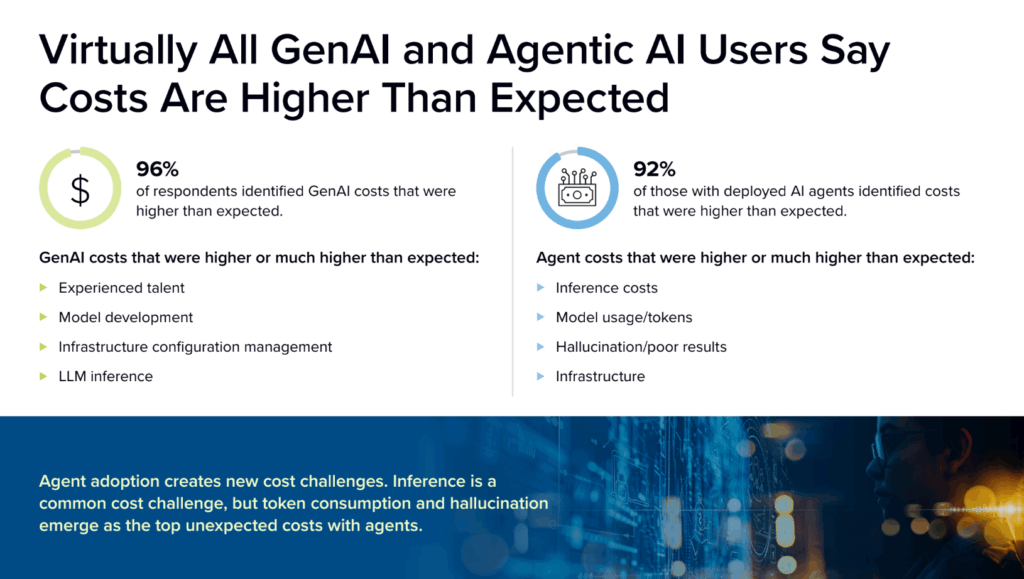
- 96% of organizations deploying generative AI report costs higher than expected
- 71% admit they have little to no control over the source of those costs.
The competitive gap is no longer about build speed. It is about who can operate a safe, “Tier 0” service foundation in any environment.
The high cost of complexity: why pilots fail to scale
The “hidden AI tax” is not a one-time fee; it is a compounding financial drain that multiplies as you move from pilot to production. When you scale from 10 agents to 100, a lack of visibility and governance turns minor inefficiencies into an enterprise-wide cost crisis.
The true cost of AI is in the complexity of operation, not just the initial build. Costs compound at scale due to three specific operational gaps:
- Recursive loops: Without strict monitoring and AI-first governance, agents can enter infinite loops of re-reasoning. In a single night, one unmonitored agent can consume thousands of dollars in tokens.
- The integration tax: Scaling agentic AI often requires moving from a few vendors to a complex web of providers. Without a unified runtime, 48% of IT and development teams are bogged down in maintenance and “plumbing” rather than innovation (IDC).
- The hallucination remediator: Remediating hallucinations and poor results has emerged as a top unexpected cost. Without production-focused governance baked into the runtime, organizations are forced to retrofit guardrails onto systems that are already live and losing money.
The production wall: why agentic AI stalls in production
Moving from a pilot to production is a structural leap. Challenges that seem manageable in a small experiment compound exponentially at scale, leading to a production wall where technical debt and operational friction stall progress.
Production reliability
Teams face a hidden burden maintaining zero downtime in mission-critical environments. In high-stakes industries like manufacturing or healthcare, a single failure can stop production lines or cause a network outage.
Example: A manufacturing firm deploys an agent to autonomously adjust supply chain routing in response to real-time disruptions. A brief agent failure during peak operations causes incorrect routing decisions, forcing multiple production lines offline while teams manually intervene.
Deployment constraints
Cloud vendors typically lock organizations into specific environments, preventing deployment on-premises, at the edge, or in air-gapped sites. Enterprises need the ability to maintain AI ownership and comply with sovereign AI requirements that cloud vendors cannot always meet.
Example: A healthcare provider builds a diagnostic agent in a public cloud, only to find that new Sovereign AI compliance requirements demand data stay on-premises. Because their architecture is locked, they are forced to restart the entire project.
Infrastructure complexity
Teams are overwhelmed by “infrastructure plumbing” and struggle to validate or scale agents as models and tools constantly evolve. This unsustainable burden distracts from developing core business requirements that drive value.
Example: A retail giant attempts to scale customer service agents. Their engineering team spends weeks manually stitching together OAuth, identity controls, and model APIs, only to have the system fail when a tool update breaks the integration layer.
Inefficient operations
Connecting inference serving with runtimes is complex, often driving up compute costs and failing to meet strict latency requirements. Without efficient runtime orchestration, organizations struggle to balance performance and value in real time.
Example: A telecommunications firm deploys reasoning agents to optimize network traffic. Without efficient runtime orchestration, the agents suffer from high latency, causing service delays and driving up costs.
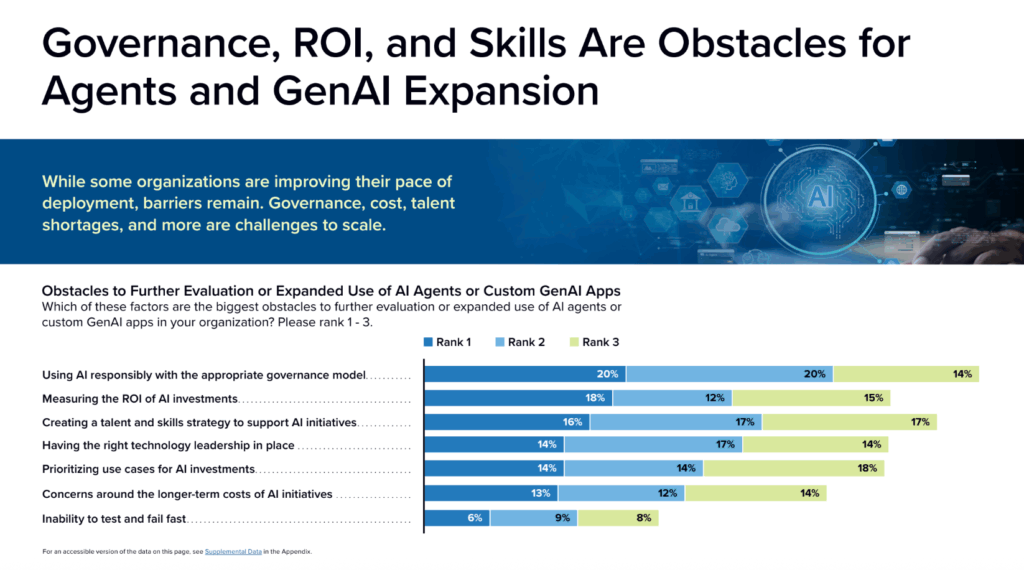
Governance: the constraint that determines whether agents scale
For 68% of organizations, clarifying risk and compliance implications is the top requirement for agent use. Without this clarity, governance becomes the single biggest obstacle to expanding AI.
Success is no longer defined by how fast you experiment, but by your ability to focus on productionizing an agentic workforce from the start. This requires AI-first governance that enforces policy, cost, and risk controls at the agent runtime level, rather than retrofitting guardrails after systems are already live.
Example: A company uses an agent for logistics. Without AI-first governance, the agent might trigger an expensive rush-shipping order through an external API after misinterpreting customer frustration. This results in a financial loss because the agent operated without a policy-based safeguard or a “human-in-the-loop” limit.
This productionization-focused approach to governance highlights a key difference between platforms designed for agentic systems and those whose governance remains limited to the underlying data layer.
Building for the 100 agent benchmark
The 100-agent mark is where the gap between early movers and the rest of the market becomes a permanent competitive divide. Closing this gap requires a unified platform approach, not a fragmented stack of point tools.
Platforms built for managing an agentic workforce are designed to address the operational challenges that stall enterprise AI at scale. DataRobot’s Agent Workforce Platform reflects this approach by focusing on several foundational capabilities:
- Flexible deployment: Whether in the public cloud, private GPU cloud, on-premises, or air-gapped environments, ensure you can deploy consistently across all environments. This prevents vendor lock-in and ensures you maintain full ownership of your AI IP.
- Vendor-neutral and open architecture: Build a flexible layer between hardware, models, and governance rules that allows you to swap components as technology evolves. This future-proofs your digital workforce and reduces the time teams spend on manual validation and integration.
- Full lifecycle management: Managing an agentic workforce requires solving for the entire lifecycle — from Day 0 inception to Day 90 maintenance. This includes leveraging specialized tools like syftr for accurate, low-latency workflows and Covalent for efficient runtime orchestration to control inference costs and latency.
- Built-in AI-first governance: Unlike tools rooted purely in the data layer, DataRobot focuses on agent-specific risks like hallucination, drift, and responsible tool use. Ensure your agents are safe, always operational, and strictly governed from day one.
The competitive gap is widening. Early movers who invest in a foundation of governance, unified tooling, and cost visibility from day one are already pulling ahead. By focusing on the digital agent workforce as a system rather than a collection of experiments, you can finally move beyond the pilot and deliver real business impact at scale.
Want to learn more? Download the research to discover why most AI pilots fail and how early movers are driving real ROI. Read the full IDC InfoBrief here.
