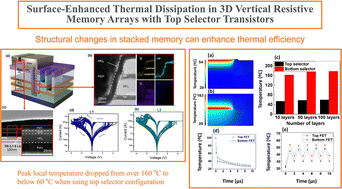
Recent integration of 3D memory technologies such as high-bandwidth memory [HBM] into AI accelerators has enhanced neural network performance. However, the stacked structures of 3D memories result in notable heat accumulation because lateral interfaces obstruct vertical heat dissipation, thereby hindering effective cooling. An effective approach to mitigating energy consumption involves the utilization of nonvolatile memory technologies, such as resistive random-access memory (RRAM). Integration of selector transistors with RRAM devices mitigates sneak path leakage, increases nonlinearity, and improves the reliability of vertically stacked arrays. Nevertheless, executing core AI tasks—such as vector-matrix multiplication in neuromorphic computing—requires substantial current flow through these transistors, which in turn leads to heat generation, reduced power efficiency, and potential computational errors. Additionally, densely stacked layers create hotspots and restrict access to cooling interfaces. This study presents a comparative analysis of models with various selector transistor configurations, based on power parameters from microfabricated 3D RRAM structures. The results indicate that optimally positioning the selector transistor at the memory interface can reduce nanoscale heat accumulation by up to 11%, as verified through finite-element simulations and numerical calculations. Improved thermal management reduced peak local temperatures from over 160 °C to below 60 °C within 20 nanoseconds in configurations featuring 10 to 100 stacked layers.