In the previous tutorials, we explored how Foundation Models work in iOS 26 and how you can start building AI-powered features using this new framework. We also introduced the @Generable macro, which makes it easy to convert generated responses into structured Swift types.
Now, in Part 3 of the Foundation Models series, we’ll dive into another powerful capability: Tool Calling — a feature that lets the model interact with your app’s functions to perform tasks, retrieve data, or trigger actions based on user input.
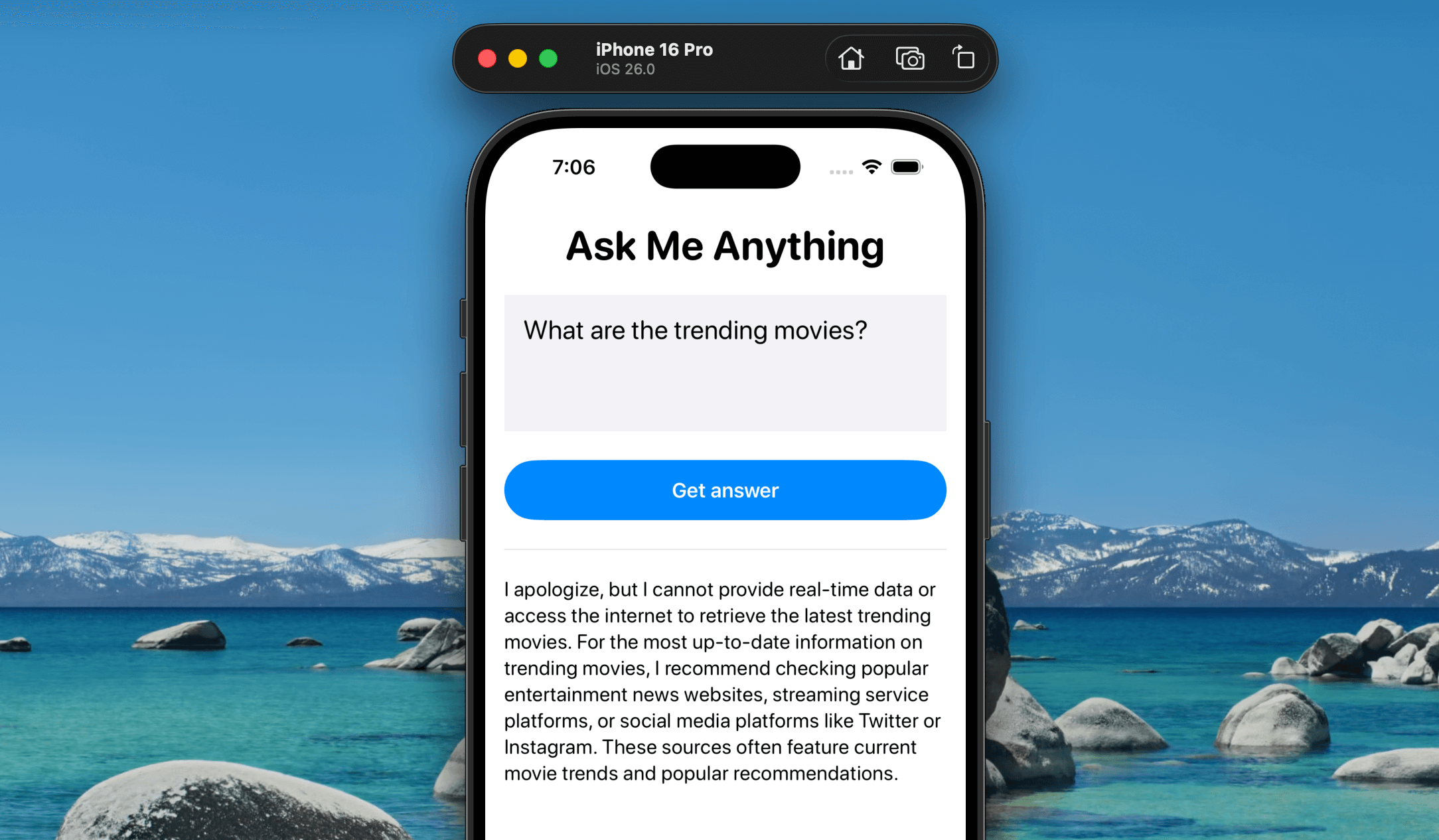
The on-device language model isn’t capable of answering every type of question, especially those that require real-time data, like the current weather or the latest stock prices. In other cases, you might want the model to access your app’s own data to respond accurately. That’s where Tool Calling comes in that it allows the model to delegate specific tasks to your app’s functions or external APIs.
In this tutorial, we’ll extend the Ask Me Anything app. While the on-device model can handle general queries, it doesn’t have access to up-to-date information about trending movies. To bridge that gap, we’ll use Tool Calling to integrate with the The Movie Database (TMDB) API, enabling the model to respond to movie-related questions using live data.
Using TMDB APIs
If you ask the Ask Me Anything app about trending movies, the on-device language model won’t have the answer—it simply doesn’t have access to that kind of real-time information and may suggest checking other sources instead. Let’s fix that using Tool Calling and the TMDB API. With this setup, whenever a user asks a movie-related question, the model won’t respond with “I don’t know.” Instead, it will automatically call the external API and return the relevant information directly in the app.
In the Xcode project, create a MovieService file and insert the following code:
// Model for a Movie
struct Movie: Codable, Identifiable {
let id: Int
let title: String
let overview: String
// Coding keys to match API response
enum CodingKeys: String, CodingKey {
case id
case title
case overview
}
}
// Model for the API response
struct TrendingMoviesResponse: Codable {
let results: [Movie]
}
// Service class to fetch trending movies
class MovieService {
// Base URL for TMDB API
private let baseURL = "
private let apiKey = ""
// Function to fetch trending movies using async/await
func fetchTrendingMovies() async throws -> [Movie] {
// Construct the URL for trending movies
let urlString = "\(baseURL)/trending/movie/day?api_key=\(apiKey)"
guard let url = URL(string: urlString) else {
throw URLError(.badURL)
}
// Perform the network request
let (data, response) = try await URLSession.shared.data(from: url)
// Check for valid HTTP response
guard let httpResponse = response as? HTTPURLResponse,
(200...299).contains(httpResponse.statusCode) else {
throw URLError(.badServerResponse)
}
// Decode the JSON response
let decoder = JSONDecoder()
let trendingResponse = try decoder.decode(TrendingMoviesResponse.self, from: data)
return trendingResponse.results
}
}
Make sure you replace the value of apiKey with your own TMDB API key. If you haven’t signed up yet, head over to themoviedb.org and register for a free account to get your API key.
The code above is fairly straightforward: it calls the web API to fetch trending movies, then parses the response and decodes it into an array of Movie objects.
Next, we’ll use Tool Calling to trigger the code in MovieService whenever the user asks about trending movies. To get started, create a new file named GetTrendingMoviesTool.swift and add the following code:
import FoundationModels
struct GetTrendingMoviesTool: Tool {
let name = "getTrendingMovies"
let description = "Get trending movies and their information"
let service = MovieService()
@Generable
struct Arguments {
}
func call(arguments: Arguments) async throws -> [String] {
let movies = try await service.fetchTrendingMovies()
let formattedMovies = movies.map { movie in
"\(movie.title): \(movie.overview)"
}
return formattedMovies
}
}
We define a GetTrendingMovieTool struct that conforms to the Tool protocol — this is the standard way to implement Tool Calling in the Foundation Models framework. The protocol requires you to specify a name and description for the tool, along with an Arguments struct to represent any parameters the tool might need. In this case, we don’t require additional input, so we define an empty Arguments structure.
If you wanted to filter trending movies by genre, you could define Arguments like this:
@Generable
struct Arguments {
@Guide(description: "The genre to fetch trending movies")
var genre: String
}
When the tool is triggered by the model, the call method is automatically executed. Inside it, we call the fetchTrendingMovies() method from our service. After receiving the results, we format them to display each movie’s title and overview.
With the trending movie tool in place, integrating it into your app is straightforward. Simply open ContentView and update the LanguageModelSession initialization as follows:
@State private var session = LanguageModelSession(tools: [GetTrendingMoviesTool()])
You can provide custom tools by passing them through the tools parameter when initializing the language model session. That’s it! The language model will automatically invoke GetTrendingMoviesTool whenever it detects a question related to trending movies.
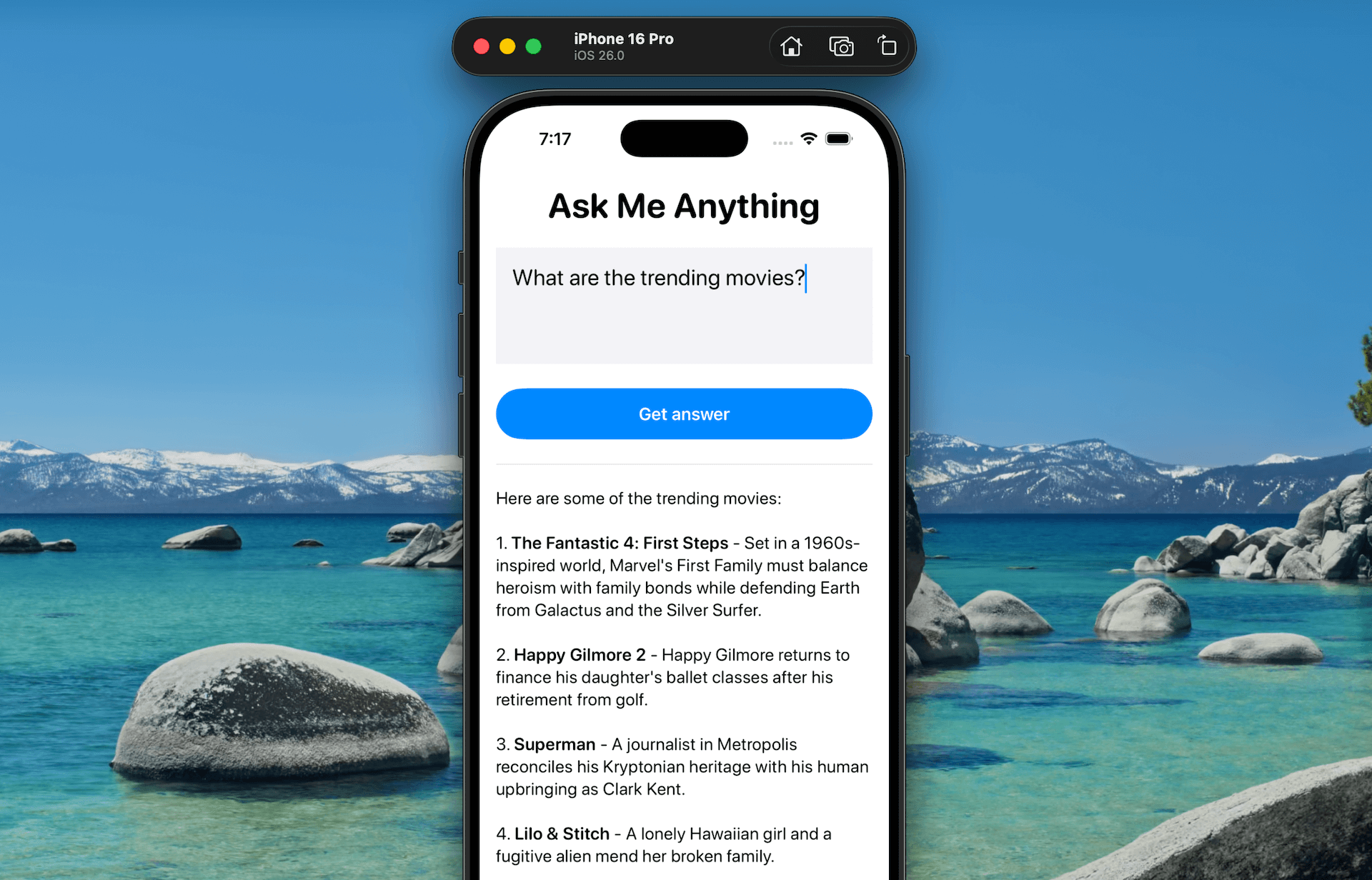
Build and run the app, then try asking the same question again. This time, the model will successfully respond with trending movie information by invoking the tool.
Summary
In this tutorial, we explored tool calling, a powerful addition to the Foundation Models framework in iOS 26. Unlike basic text generation, tool calling enables the on-device language model to interact with your app’s functions or access external services.
With tool calling, you can significantly extend the model’s capabilities. Whether it’s running custom logic or fetching real-time data through APIs, the model can now perform context-aware tasks beyond its built-in knowledge.
I hope you’ve enjoyed this tutorial series and feel inspired to start building smarter, AI-powered features using the Foundation Models framework.

