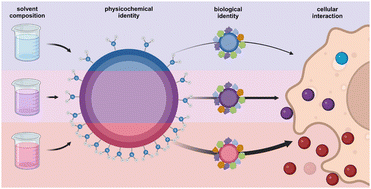
Precise control over surface properties is crucial for the design of nanocarriers in biomedical applications. These properties influence biological interactions. Functional co-monomers can be used to tailor the surface chemistry of nanocarriers synthesized in radical heterophase polymerization in aqueous phase. However, achieving similar control over nanocarriers derived from natural materials in inverse miniemulsion, such as protein nanocapsules, remains challenging. Here, we demonstrate how the surface functional group density of protein nanocapsules can be tuned systematically by varying the hydrophobicity of the continuous phase during the synthesis via the click reaction between hydrophilic azide-modified proteins and a hydrophobic dialkyne crosslinker. By adjusting the solvent mixture of toluene and cyclohexane, the interfacial properties of the droplets are modified, influencing the partial denaturation of the protein and orientation of the amine-terminated lysine residues. This, in turn, affects the accessibility of the azide groups for the crosslinking. Changes in solvent composition furthermore influence the solubility and reactivity of the crosslinker, thereby modulating the degree of azide functionalization. This allows for precise control over the number of unreacted azide groups available for subsequent biorthogonal click reactions. We demonstrate that the multifunctional surface, with amine, azide and alkyne groups, enables the simultaneous attachment of different molecules to the nanocapsule. Finally, we show that while changes in continuous phase hydrophobicity lead only to minor changes in protein corona composition, they significantly affect macrophage uptake, likely due to differences in surface amine density. Our combined findings provide a novel approach for tailoring the surface functionality of nanocapsules, facilitating more precise and versatile biofunctionalization strategies, particularly for targeted drug delivery.