mall uses Large Language Models (LLM) to run
Natural Language Processing (NLP) operations against your data. This package
is available for both R, and Python. Version 0.2.0 has been released to
CRAN and
PyPi respectively.
In R, you can install the latest version with:
In Python, with:
This release expands the number of LLM providers you can use with mall. Also,
in Python it introduces the option to run the NLP operations over string vectors,
and in R, it enables support for ‘parallelized’ requests.
It is also very exciting to announce a brand new cheatsheet for this package. It
is available in print (PDF) and HTML format!
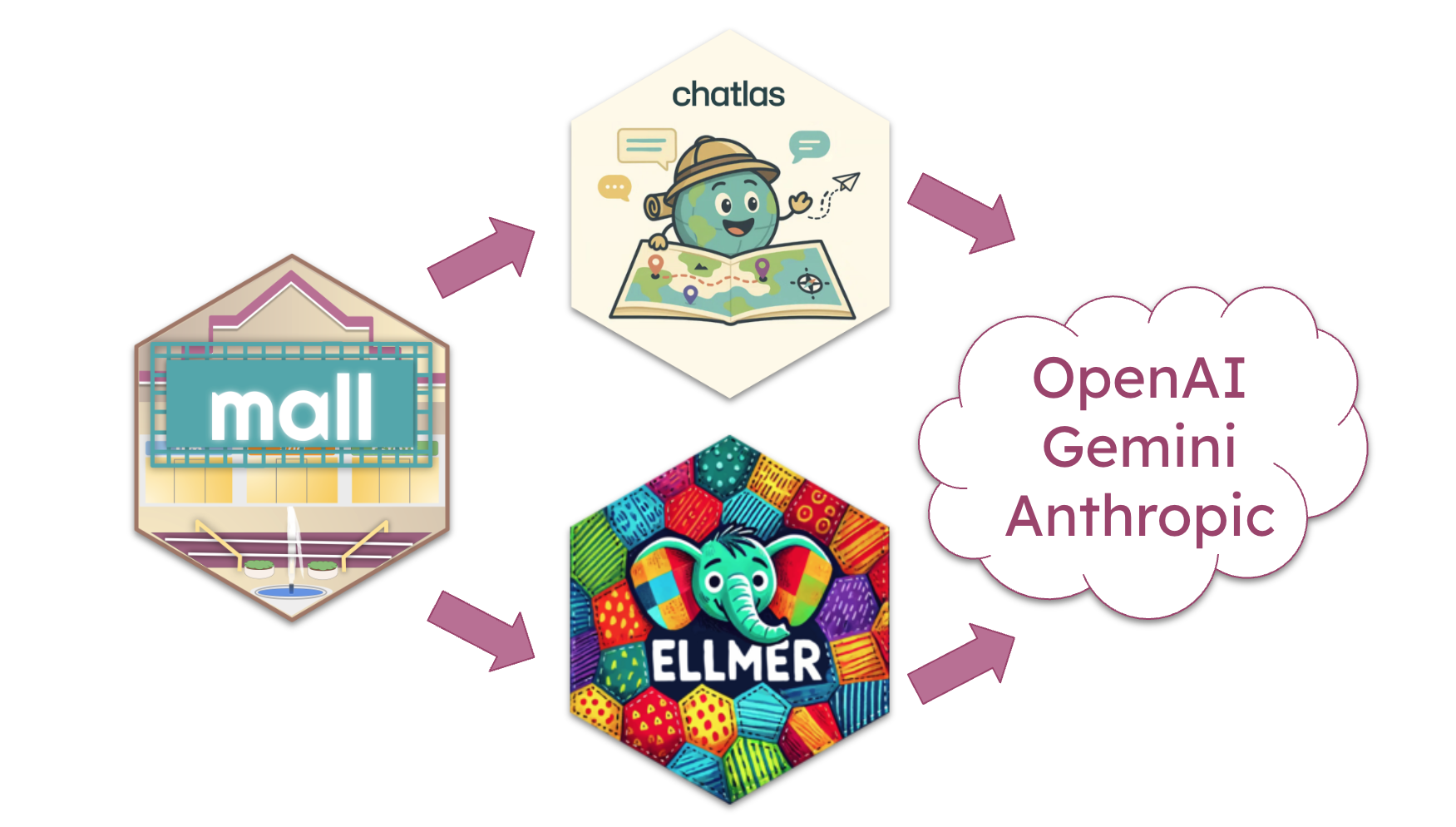
More LLM providers
The biggest highlight of this release is the the ability to use external LLM
providers such as OpenAI, Gemini
and Anthropic. Instead of writing integration for
each provider one by one, mall uses specialized integration packages to act as
intermediates.
In R, mall uses the ellmer package
to integrate with a variety of LLM providers.
To access the new feature, first create a chat connection, and then pass that
connection to llm_use(). Here is an example of connecting and using OpenAI:
install.packages("ellmer")
library(mall)
library(ellmer)
chat <- chat_openai()
#> Using model = "gpt-4.1".
llm_use(chat, .cache = "_my_cache")
#>
#> ── mall session object
#> Backend: ellmerLLM session: model:gpt-4.1R session: cache_folder:_my_cacheIn Python, mall uses chatlas as
the integration point with the LLM. chatlas also integrates with
several LLM providers.
To use, first instantiate a chatlas chat connection class, and then pass that
to the Polars data frame via the
pip install chatlas
import mall
from chatlas import ChatOpenAI
chat = ChatOpenAI()
data = mall.MallData
reviews = data.reviews
reviews.llm.use(chat)
#> {'backend': 'chatlas', 'chat': Connecting mall to external LLM providers introduces a consideration of cost.
Most providers charge for the use of their API, so there is a potential that a
large table, with long texts, could be an expensive operation.
Parallel requests (R only)
A new feature introduced in ellmer 0.3.0
enables the access to submit multiple prompts in parallel, rather than in sequence.
This makes it faster, and potentially cheaper, to process a table. If the provider
supports this feature, ellmer is able to leverage it via the
parallel_chat()
function. Gemini and OpenAI support the feature.
In the new release of mall, the integration with ellmer has been specially
written to take advantage of parallel chat. The internals have been re-written to
submit the NLP-specific instructions as a system message in order
reduce the size of each prompt. Additionally, the cache system has also been
re-tooled to support batched requests.
NLP operations without a table
Since its initial version, mall has provided the ability for R users to perform
the NLP operations over a string vector, in other words, without needing a table.
Starting with the new release, mall also provides this same functionality
in its Python version.
mall can process vectors contained in a list object. To use, initialize a
new LLMVec class object with either an Ollama model, or a chatlas Chat
object, and then access the same NLP functions as the Polars extension.
# Initialize a Chat object
from chatlas import ChatOllama
chat = ChatOllama(model = "llama3.2")
# Pass it to a new LLMVec
from mall import LLMVec
llm = LLMVec(chat) Access the functions via the new LLMVec object, and pass the text to be processed.
llm.sentiment(["I am happy", "I am sad"])
#> ['positive', 'negative']
llm.translate(["Este es el mejor dia!"], "english")
#> ['This is the best day!']For more information visit the reference page: LLMVec
New cheatsheet
The brand new official cheatsheet is now available from Posit:
Natural Language processing using LLMs in R/Python.
Its mean feature is that one side of the page is dedicated to the R version,
and the other side of the page to the Python version.

An web page version is also availabe in the official cheatsheet site
here. It takes
advantage of the tab feature that lets you select between R and Python
explanations and examples.